Alzheimer Disease Case Study Solution
Histology/Histopathology of Alzheimer Disease:
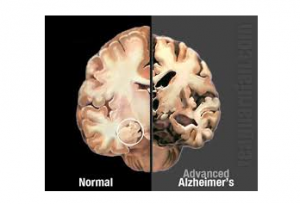
A person having Alzheimer’s will face the loss of synapses (the signals that neurons pass to each other) in the largest segment of the cerebrum, cerebral cortex. Because the neurons fail to connect with each other, it becomes the cause of atrophy and the decaying of the temporal lobe and parietal lobe. Because of this, the brain starts to shrink. The picture below shows the size of a brain of a normal person in comparison to the size of a brain of an Alzheimer’s patient.
Though today experts are not sure that what the cause of Alzheimer is, but neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are considered to be one of the reasons behind it.
Neuritic Plaques and Neurofibrillary Tangles:
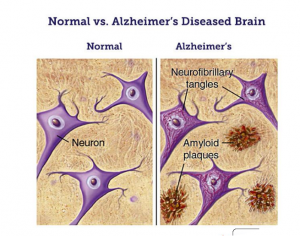
Neuritic plaques also known as senile plaques are discharged by amyloid beta (a protein which is a component of neurons) outside the cell in the grey matter of the brain. Neuritic plaques are also associated with the change of tissue, in which it becomes less active and performs fewer functions. These plaques are made of amyloid beta peptides in Alzheimer’s. They form a cluster of beta-amyloid and stick with the walls of neurons. Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are developed due to the hyper phosphorylation of tau, a sticky protein. These proteins becomedamaged and are suspected to be a cause of Alzheimer’s. Neurofibrillary tangles make a clump together and take the shape of tangles. Both of these interfere in the functioning of neuron cells. Research done on animal’-s shows that the plaques and tangles form automatically because of infection in thebrain.This research suggests that maybe Alzheimer’s is related to some type of brain infection. (neuropathology, 2017)
The below diagram shows a brain with Alzheimer’s and what neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles looks like.
Synaptic Loss
A forty-five percent loss of synapses was recorded in the brain of a patient of Alzheimer’s in comparison to a normal human brain. This loss is the main cause that neurons cannot connect with each other and because of this, the bodily functions are not conducted actively. (Med, 2010)
Epigenetics of Alzheimer Disease:
Epigenetics is the study of changes in genes; active genes and inactive genes. These changes occur because of the aging factor, change in environment or because of some disease. (.whatisepigenetics, 2017)
A lot of cases of Alzheimer’s are connected with changes in genetics but a large number of these cases do not illustratesolid genetic underpinnings and that’s why are thought to be associated with non-genetic factors. Genome-wide epigenetic variations are testified. Genes that are related to Alzheimer disease show epigenetic alterations, directing that epigenetics might use a pathogenic part in Alzheimer’s. These alterations can be changed and are reversible. Mutations in a number of enzymes of the epigenetic machinery isrelatedto the process of decaying of neurons that are changed in Alzheimer’s, for example, reduced learning and weak memory...........
This is just a sample partial work. Please place the order on the website to get your own originally done case solution.