Energy Economics Case Study Solution
Content and Analysis
In order to understand and analyze the pros and cons of full retail contestability, the electricity market needs to be thoroughly analyzed and how the changes will affect the market needs to be understood.
The market has had laws to make the market efficient and effective. In 1945 the government passed a law named Electricity Act 1945, according to which the law assesses a person’s competency to work in the energy sector. Then in 1947 another law was passed to assess
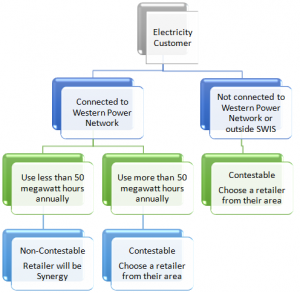
In Exhibit 1 the figure shows how the electricity consumer is categorized into the sets that the government and regulations have established. The very first categorization is if the user is a part of the Western Power or not. SWIS has a huge covered area and in that area Synergy or Horizon Power operates only. If the user falls under the SWIS then his usage is assessed, if the usage of electricity is more than 50 megawatts per hour the customer gets to choose the retailer these customers consists of 60 percent of the market share,otherwise he will get the services of Synergy (remaining 40 percent). But if the user does not fall under SWIS the user is allowed to choose the retailor that he wants.
The market has some main players that run the market. The first are the on-supply retailers, they take the energy from generators (Synergy) and pass it on to the tenants. They use their main meter to obtain the electricity and passes the electricity to the other sub-meters of his tenants. These retailors do not earn a lot as they have to incur the maintenance costs, and they are not allowed to charge above the stated price by government. These retailors are obliged to have a license to do so under the Electricity Industry Act 2004. (On-supply of electricity).
This liscene is necessay for the generators of electricity, they cannot generate electricity without this liscene. The generators generate the electricity under the Electricity Industry Act and supply the electricity to households and businesses. The private generators are allowed to cater the contestable group which consists the group of people who own businesses that consume more than 50 megawatts/hour or they are out of the SWIS coverage. These companies had to compete amongs themselves to gain the highest market share after Synergy who was collaborated with SWIS. They used to cater the larger market that consisted of all the households and small businesses.
IMO stands for independent market operator, this is a industry funded organisation, they have an aim is to make the market a competitive place.They motivate the private companies to bring in their efforts and help them feel more secured and safe. They provide the latest information and maintains a transperencey in the market place.
There are three mechanisms of the market. The first is the bilateral trade of energy which specifies the group that share the market and trade energy without involving a thrid party, second is the short tern energy market, these generators buy or sell the enerygy to the Indepndent Market Operator (IMO). The transaction is done a day before the delivery. The third mechanism is the balancing mechanism, this is where each generator has to contribute an amount of energy. (THE SOUTH WEST INTERCONNECTED SYSTEM WHOLESALE ELECTRICITY MARKET: AN OVERVIEW , 2006)
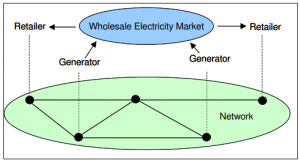
If the country implements the full retail contestability the market will become as shown in Exhibit 2. The retailors can then demand the supply from any generator that serve them on the negotiated price, this way the dominance of Synergy will end. The market will become competitive and the generators will not be able to penetrate the market with higher prices.
Government has always intervened in the energy regulations and in order to deal with the electricity supply the government has regulated prices of Synergy and Horizon Power. This way the non-contestable customers will be provided with electricity at a particular price. This also gives a benchmark to the private generators and they try to charge according to these companies or lower than them.
The government of Australia has planned to constrain the market according to a report. They plan to limit the distribution of electricity that is dispatched by the generators. If the government does so the generators will have to deal with the market operator and the electricity disposal and production will then be limited. (Utz, 2018)
According to another report the government of Australia has denied the idea to end Synergy’s monopoly and they want the energy market to function as before. (Mercer, 2018)The pressure on the government was built by the unions and they were questioned about the success of full time contestability’s success. Apart from the monopoly that Synergy has in the market, they also provide unique services to the people like in 2016 they installed solar pannels on houses for the people to produce and use their own energy. This way they stay in lead of the market. In 2017, Synergy has planned to collaborate with a private sector investor and establishing a wind mill farm where they can generate more electricity by the help of wind turbines.
Conclusion
The introduction of full retail contestability will break the monopoly of Synergy but it has been implemented in the east coast and the prices have hyped. This will also give access to the market for the new entrants. People would want to settle in Western Australia and start businesses as they will have the choice to choose the retailor they want.
But this can go the other way as well and the energy producers can demand the price they like in the areas where they have the monopoly.The generators are few in the market and the covered area is large, this will lead to monopoly where the other generators would not be able to reach.
Secondly, Synergy does not stay in the lead of the market only because it caters a larger market and the other company gets to deal with the niche market but they also enjoy success because they cater the market in the best possible way. If the government allows the people to opt for the electricity suppliers they choose, they will lose the control and the subsidies that the government has been providing will not be provided or distributed fairly.
The decision of making the people their own bosses and allowing them to make a decision of which retailer they want to deal with is very attractive, but this decision will have its own consequences. The best example is the east coast of Australia where the people are suffering due to hyped electricity prices and the government seems helpless in the region to control the prices. It would be best to let the Synergy stay in monopoly and the government should keep a budget in which the company has to produce and provide the electricity. This will keep the prices low and Synergy won’t misuse their position as a monopoly company.
Exhibit 1:
Exhibit 2:
This is just a sample partical work. Please place the order on the website to get your own originally done case solution