Future of Procurement Case Study Solution
Supporting Evidences:
Introduction of artificial intelligence in strategic procurement will be the ultimate choice. In a survey conducted by Roland Berger of 87 Chief Procurement Officer of Global Fortune 500 companies, 67% of them ranked AI as one of the top 3 priorities in the next 10 years.
According to Niul Burton, a stronger procurement capability will be enabled by digital technologies in the coming years. He mentioned in his article that,contribution of procurement will be a key driver for competitive advantage to the overall organization. The leading procurement function will also become a part of the organizations value stream.This will be more influential in the contribution of the growth agenda and the overall business strategy. He also stated that procurement would be a small and centralized function with more happening in virtual center. Needs for increased collaboration can be met by locating people geographically within business units. Machines would clean and curate their own data while real time tracking will be enabled through the data gathered from the internet. Most organizations will strictly monitor their suppliers through various sources of internal and external data, enabling the historical performance of the suppliers to be visible while making it convenient to build supplier risk profiles.He further mentioned that block chain will also be selectively used along with robotic process automation which helps to remove high volume of repeatable tasks. Purchasing experiences for goods and services will be voice activated, supported by virtual assistants and natural language search.(Burton, 2018)
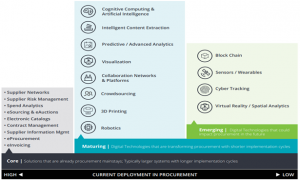
A study conducted by Deloitte highlights some Procurement technologies that are evolving rapidly, from emerging, to the maturing stage, until they are widely adopted as core solutions. (Figure 1, Appendix A)
Some of the emerging technologies are
- Block Chain: It’s a cryptologic structure of data that uses a trusted peer-to-peer network in creating digital transaction ledgers. These are used to verify and validate the transactions in the P2P processes and then used for triggering automated payment.
- Sensors or Wearables: These devices are responsible to detect, capture, and record all the available physical data. These will also be used to monitor movements of goods and levels of inventory for reordering.Along with enabling audit tracking while visiting sites.
- Cyber tracking: Real time tracking can be used for online and physical activity to provide proactive monitoring of performances supplier behavior.
- Virtual Reality: Detecting events or change in status using videos, pattern analysis, or location data, and conducting visits to supplier and auditors will empower procurement professional to do more with less.(Mike Daher, 2017)
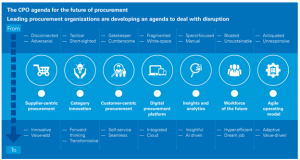
From a research conducted by KPMG it is obvious that leading procurement organizations are moving into the future with a focus on innovation, decentralized operating model to support the business and supplier and customer relationships. (Figure 2, Appendix B) shows how different disruptions will dealt with in the coming future. Few are as following:
- Supplier-centric procurement: In future procurement will be dependent on developing new operating models to support supplier centricity. One that drives supplier performance to a new level, while fostering innovation and mitigating risks.
- Category innovation: Untapped value will be unlocked by category innovation through automation, deep insights, and Predictive AI and data analytics.
- Customer-centric procurement: Customer centricity will be focused in all aspects of procurement, including systems, processes, and people. Procurement will not act as a gatekeeper, and business partners will recognize its value and will want to work with them.
- Digital procurement platform: Manually intensive and administrative tasks will be replaced by new technology, which will enable self-service. Allowing the procurement professionals to focus on the higher value of activities that in turn focuses on suppliers and customers.
- Workforce of the future: An augmented skill set is needed in the people working for procurement. Commercial acumen will be a staple, but being empathetic and technology conversant will become minimum requirements to work in the field of procurement.(kpmg, 2019).
Conclusion:
Businesses are no longer as usual for procurement. The speed and scaling of transformation that impacts procurement is unprecedented. In 2040, procurement will be quite different as compared to that of now due to increase in technology and digital advancements.
Appendix A
Figure 1: Deloitte – 2017 (Source)
Appendix B
Figure 2: KPMG – 2019 (Source)