Reawakening the World’s Most Famous Office Building: Economics behind a Ground-breaking Energy Efficiency Retrofit Case Study Solution
Energy – Efficient Retrofits:
Pros:
- Presence of green buildings in appropriate locations can significantly provide zero utility bills with the cooperation of sun and rain.
- Building of green buildings tend to be healthier by means that they are potentially built using natural products which are less dangerous.
- In context to the material used in the green building, they have increased lifespan to provide an improved return on investment.
Cons:
- Building of Green home is often costlier up front, requires balancing of increase in the cost of construction with the potential of long-term saving.
- Components of cooling utilize natural resources lacking the complete control over temperatures.
- Requirement of high cost on the basis of accurate figures on the costs of long-term usage and construction.
Industry drivers for Energy – Efficient Retrofits:
Converging Forces:
- Recognition of requirement for development more sustainable and practices of efficient business.
- Acceptance of constraints of supply chain and issues of national security posed by the dependence of energy.
- Ongoing local, state and federal legislative action.
- Organizational trend towards the reporting of GRI, self-regulation and reduction in emission of GHG.
- Pressures by shareholders, employee and customers.
Business Opportunity:
- Increased pressure for alteration of appraisals, values to lend and purchase on the basis of sustainability.
- Reduction in the cost of operations through efficiency.
- Increase in competitiveness and marketability.
- Improvement in the environment of workplace, its productivity, recruitment and retention.
- Positive ROI and NPV.
- Improvement in funds through saving of energy.
- Maintenance of value.
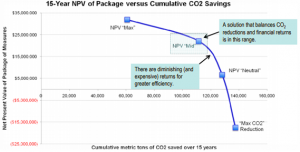
Determination of right trade-off:
Determination of right trade-off between financial return and reduction in carbon dioxide is evaluated (Appendix A) for better identification of the exact point serving as most suitable and appropriate one to be considered. Therefore, NPV is known to decrease with increase in the reduction of CO2emission. Complete reduction in the emission of greenhouse gases can only be achieved with a great negative value of NPV which at any cost cannot be considered feasible. With respect to 15 year plan in comparison to cumulative savings of CO2, the balance between financial returns and reduction in emission of CO2evaluated to be in the midpoint of NPV.As the NPV and reduction in GHG emission was known to be inversely proportional to one another effectively influencing the potential of sustainability approach as well as rate of increase in generation of revenue.
Recommendation:
With respect to the analysis of the approaches and their potential to be success with least possibility of any losses, two projects were considered to choose what to pursue i.e. green technology and Energy – Efficient retrofits. Therefore, on the basis of their pros and cons, it has been better understood to adopt energy efficient retrofits. However, both the approaches require high investment cost but greener technology seems to require research for new partners which might tend to be a great risk and is time consuming as well.
Conclusion:
The Empire State Building and some other projects suggested few possible techniques that can be considered by different corporations. Therefore, both commercial building and residential investors are seeking out for properties that are energy efficient in order to save money and reduction in carbon footprint. On the other hand, NPV is known to decrease with increase in the reduction of CO2emission. Hence, on the basis of their pros and cons, it has been better understood to adopt energy efficient retrofits. Similarly, the balance between financial returns and reduction in emission of CO2evaluated to be in the midpoint of NPV.
Appendices
Appendix A – Determination of right trade-off
Appendix B – Green vs Energy Efficient Project:
| Green Technology | Energy Efficient Retrofits |
| Renewable and recyclable | Reduction in loads |
| Indoor quality of air | Reduction in use of energy resources |
| Recycling Programs | Optimize efficiency of systems |
| Conservation of energy | Quantifiable metrics |
| Green Cleaning | Guaranteed savings |
| Integrated management of pest | Measured payback and ROI |
Appendix C – Industry drivers for Energy – Efficient Retrofits:
Appendix D – Relation between NPV and reduction in CO2 emission
This is just a sample partical work. Please place the order on the website to get your own originally done case solution.
How We Work?
Just email us your case materials and instructions to order@thecasesolutions.com and confirm your order by making the payment here