(IHA): Project Selection Theory and Practice Case Study Help
Project Selection
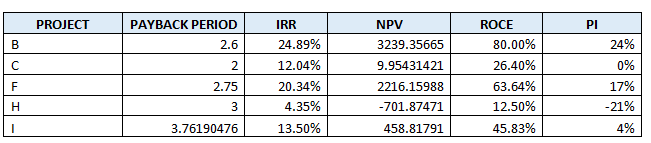
The following financial data has been identified for five independent opportunities, and we wish
to evaluate their desirability. Let us assume that interest rate is 12%. The projects net after tax and
Cash flows are estimated as follows:
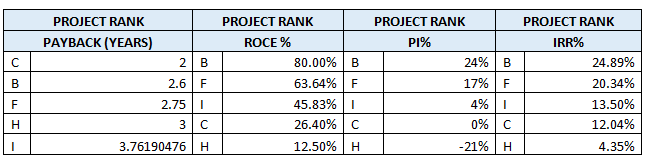
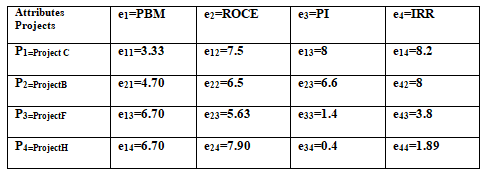
Summary of Calculations and Analysis: The following table summarizes the results produced for each project using four chosen project appraisal tools:
Projects ranking using F&SPSM
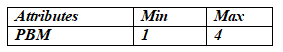
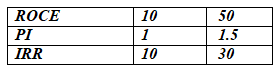
The attribute matrix should be normalised. The range for each property must be established in order to normalise data. Let us suppose that the following ranges are adequate for the given case.
Let's say the aforementioned ranges are not valid or why these values are assumed. As these numbers are used for linear transformations of given attribute values; the results are not sensitive to the choice of these ranges. All elements will be treated fairly, finding their equivalent normalized values using an agreed range of attributes. Using the normalization equation, each value should be converted into a range of 0 to 10. For ROCE, IRR and PI, the following rescaling equations should be used. For example, for the project:
The development model is a general project selection synthesis method that can be used to integrate variousevaluation techniques into project selection and evaluation. It can be used for financial analysis only or it can integrate selection models of financial and non-financial elements. It can also combine the qualitative and quantitative methods. The reflections on the model and its critical evaluation in the next section show the problems with this approach and the benefits that can be derived from the model.
Based on the results of this article’s analysis and the points raised in the literature; it can be said that there is no single and optimal model in the evaluation and selection of projects. The choice of the type and mode of method depends on the nature of the project, the nature of the investment and the attitude of the management. Most researches show that the financial models are widely used for decision making.
However, as he shows, these models can give different responses and support different options. A fair and equitable item selection model can be used to incorporate many factors (up to four at a time). These factors can be financial or a combination of financial and non-financial factors. The model can be used very easily and does not involve tedious calculations. The model is complete and there is no single financial model, such as the claw back method, which does not consider the time value of money. It is important to note that this argument is not against the financial models, as all the financial models can be used simultaneously through the MSPSF.
In addition, it should be noted that there are also problems and difficulties associated with this model. When non-financial factors are built into the model, quantification of non-financial factors is not so easy. The evaluation of managerial support for a project is very subjective and can be wrong. The idea is to ask people to translate their attitudes and feelings into numbers, a difficult if not impossible task. The next criticism of the model is the assumption that all factors are equally important. This is not necessarily true in real life. This will increase the extent to which each of these factors affect and contribute to the success of the project, which was not addressed in this study...............
(IHA) Project Selection Theory and Practice Case Study Help
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.