BUCK AUTO CARE PRODUCTS: SELLING A PRIVATE COMPANY Case Study Solution
Introduction
This case discusses the concepts of valuations and the decision-making of the management in regards of selling a private company. The company was established in 1975 as a car wash company in Toronto and Mississauga. It was a chain of car wash, and further, for increasing the revenues; Buck started other complementary care products, which later became Buck's major focus. These complementary care products were: cleaner, leather, car covers, and wax. The CFO was preparing for a meeting with the Vice President of sales and manufacturing. Buck’s staff came to know about the rumors of the company being sold, but no one had confirmed it yet. As competitors were interested in buying the company, and the CFO was working on a response to the competitors, ache was considering to address few issues before getting to the valuation.
Problem Statement
As the CFO was preparing the offer for competitors, but she was thinking to consider the preliminary issues before getting to valuation and finalizing the price. The company was considering Sentry’s offer, because there were no chances of potential growth irrespective of having full distribution in the Canadian market. The management team was also lacking in many aspects, and the company was unable to acquire amajor portion of consumers. Buck was considering this option to increase the company’s value.
Question 1
Buck was considering to sell the company. Buck continued its operations until August 2014, but Cynthia reached her 70’s and had decided to enjoy her retirement and meanwhile merger and acquisition intermediary, which was appealing. It was an appealing offer for Cynthia, as she was working with an intermediary to find a good price offer to sell the company. The intermediary was suggesting valuation methods that can help Cynthia to get a good price, which would increase her net worth. Cynthia was considering this offer because she was now willing to get retirement and she also wanted to increase the net worth of the company.
Question 2
As a Buyer, I would be willing to buyback because my personal interest and loyalty were with Buck as a brand, and not with other companies. And after the merger; I would also doubt the quality of products and services. My primary consideration would be product quality, company’s services, and overall value of the brand after the merger, and the prices of products and services. These would be my primary considerations, because as a potential consumer; I am more concerned about the other acquiring company and in knowing the values they deliver for their customers.
Question 3
Discounted cash flows model Valuation
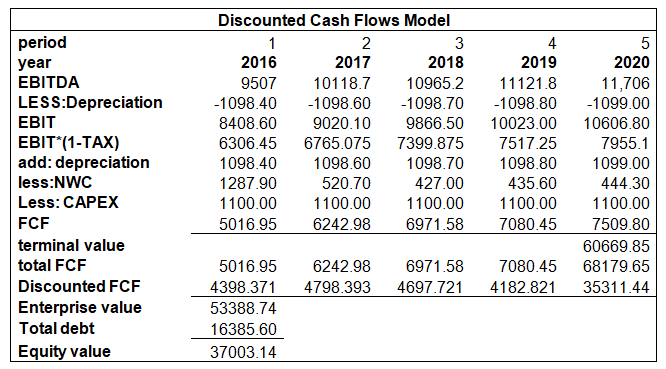
The discounted cash flow valuation model was used to calculate the value of Buck’s equity. In the DCF model; we took the weight of equity and the weight of debt from exhibit 5 given in the case. So, the weight of equity was 62% and the weight of debt was 38%. the rate of debt before tax is given in case as 6%, so the interest rate before tax is 6%, the after-tax cost of debt is 5%. The tax rate has been given in case as 25%. to calculate the rate of equity is also given in range from 20% to 25% so we assumed 20%. The calculated WACC is 14%, (given below in appendix:2). the enterprise value by using DCF is $53388740, and the equity value is $37003140. The book value of equity is $26398900 in 2015(JASON FERNANDO, 2021).
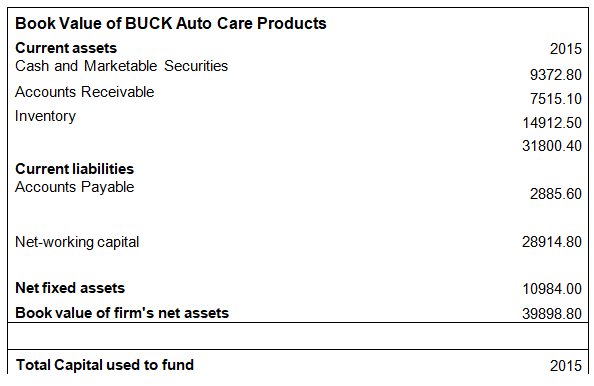
Book value vs market value
The book value of equity is $26398900 in 2015(see appendix 3). The market of the company will be equal to the market capitalization plus the total debt roebuck in the balance sheet, as Buck is a private limited firm; its shareware not trading publicly so the data on the share price and the number of shares outstanding to calculate market capitalization are not available. So, we take the market capitalization of a comparable firm in the same industry. The Venator Materials PLC is the competitor of Buck, so we took the market capitalization of this company to compare with Buck’s book value. The market value of Venator Materials PLC is $305680000 million and the book value of bucks is 39898900. So, the book value of Buck is much lower than the market value of Venator Materials PLC(NYSE Delayed Price. Currency in USD, 2021).
Market multiples
The value of Buck is evaluated by using the EV/EBITDA market multiples, which is $43123750, andits value of equity is $26738150. The book value of equity is $26398900. This shows that the market value of equity is greater than the book value of equity. On the other hand, value of equity of Buck, by using EBITDA to sales ratio, is -$10050380, which is not comparable.(See appendix 3).
The range of value is from$26738150 to $37003140,so Buck should not consider selling bellow $26738150 value of equity.
The best deal approach is the DCF model, because it is based on the estimations, and the estimation is based on the firm’s previous performance. On the other hand, market multiple approaches are based on the average performance of the industry, so they can be changed over time. The firm should base its decision on the DCF model, but it should not ignore the valuation results of multiple approaches....................
Appendices
Appendix:1 DCF model:
Appendix:2 WACC
Appendix:2 book value of Buck
Appendix:3 Market Multiples
BUCK AUTO CARE PRODUCTS SELLING A PRIVATE COMPANY Case Study Solution
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.