Road Building or Road pricing Case Solution
Introduction
Hon Kong was concerned about the rising traffic congestion in the northern region of the island that has affected severely the growing and large metropolitan regions round the world. Traffic congestions in the peak hours is an integral outcome of the way modern societies operate. The reasons that may cause traffic congestion include traffic accidents, construction activities and weather etc.
The government of Hong Kong had tried to find the solution for congestion problem by proposing to build a new road which faced strong opposition by the environmental groups. The government them considered the other possible and innovative road pricing option to solve the concerned problem. The road pricing option has been successfully implemented by other regions globally. Therefore the government has come up with the two considered solutions for the solution to congestion problem i.e. road pricing or road building.
Problem statement
The rising traffic congestion has proved to be a major problem for the large metropolitan cities across the world. Hong Kong has was also facing this problem and tried to solve it with the building of new road but the idea was strongly oppose. The other way that is used globally to reduce traffic congestion is road pricing is also being considered by the government. Hence the government has come across a road to choose between best possible way to reduce congestion from road pricing or road building.
Situational analysis
Cost and Benefit of Using Cars versus Public Transport
Various factors responsible for costs and benefits of using a car versus public transport for a commuter includes time, distances cost, personal preferences and convenience etc. (Litman, 2015). Generally, driving a car offers more flexibility and convenience, allowing commuters to save time and travel directly to their destination. However, driving also involves costs such as fuel, parking fees, tolls, maintenance, and depreciation of the car. Public transport, on the other hand, is usually cheaper, environmentally friendly, and reduces the need for parking. However, it may involve longer travel times and less flexibility. The impact of public transport is presented below.
Commuter’s Preference to Drive
Commuters may choose to drive for various reasons, such as comfort, privacy, safety concerns, or to save time. Those who live in suburban areas or have limited access to public transport may be more likely to drive to work.
Costs of Traffic and Congestion
Traffic and congestion impose various costs on society, such as increased travel time, fuel consumption, air pollution, noise pollution, and accidents. These costs can reduce the quality of life, health, and productivity of people, increase transportation costs, and harm the environment. Additionally, congestion can reduce economic growth by limiting the mobility of goods and people, leading to lost opportunities and reduced competitiveness.
Effects of EPR
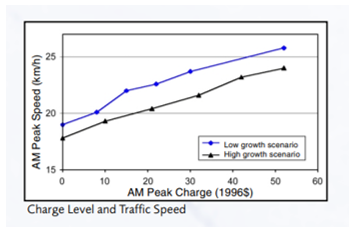
Electronic Road Pricing can have a significant effect on the urban development, town planning, residential property prices, fares charged by public transport, and labor force participation. The measure of charge is done via traffic diversion/suppression ratio as shown in below graph.
Urban Development and Town Planning
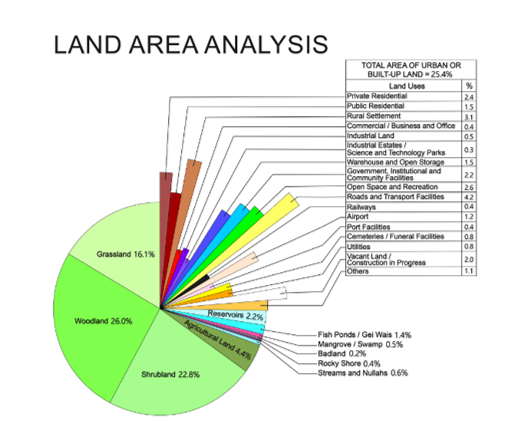
Electronic road pricing (ERP) can affect urban redevelopment and town planning by changing the travel patterns of people and businesses. By charging vehicles based on road usage and time, ERP can reduce congestion and encourage people to use alternative modes of transport. This can lead to the development of transit-oriented developments, where people live and work near public transport hubs, reducing the need for car ownership and travel. The area division is described in the below chart.
Residential Property Prices
ERP can also affect residential property prices by changing the accessibility and desirability of certain areas. Areas with better public transport links and less traffic congestion may become more attractive, leading to increased demand and higher property values. Conversely, areas with high road usage and congestion may become less attractive, leading to lower property values.
Fare Charged By Public Transport
The fare charged by public transport can be affected by ERP if it reduces the number of private cars on the road and increases the demand for public transport. If more people switch to public transport, the operating costs can be spread across more passengers, reducing the fare. However, if ERP does not lead to a significant reduction in car usage, public transport fares may remain unchanged or increase...............
This is just a sample partial case solution. Please place the order on the website to order your own originally done case solution.